What Is A Passive RFID Tag
Introduction
Welcome to the exciting world of passive RFID tags! In this article, we will delve into the definition, functionality, advantages, applications, challenges, and limitations of passive RFID tags. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or simply curious about this technology, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of passive RFID tags and their role in the modern world.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized various industries, including retail, logistics, healthcare, and transportation. It enables objects to be identified, tracked, and monitored using radio waves, offering convenience, efficiency, and accuracy.
Among the different types of RFID tags, passive RFID tags stand out for their simplicity and wide range of applications. Unlike active RFID tags that rely on an internal power source, passive RFID tags do not have a built-in power supply. Instead, they harness energy from the RFID reader’s signal to transmit data.
This article will take you on a journey to understand how passive RFID tags work, the components that make them function, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they offer. We will also explore the various applications where passive RFID tags have made a significant impact, from inventory management to access control systems.
Furthermore, we will address some of the challenges and limitations that passive RFID technology faces, including range limitations, interference issues, and privacy concerns. It is important to have a complete understanding of these factors to make informed decisions when considering the implementation of passive RFID tags.
By the end of this article, you will have gained valuable insights into the world of passive RFID tags, and hopefully, you’ll be able to appreciate the impact this technology has on our daily lives and various industries. So let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of passive RFID tags.
Definition of Passive RFID Tag
Before we dive into the intricacies of passive RFID tags, it’s important to establish a clear definition of what they are. A passive RFID tag, also known as a passive radio frequency identification tag, is a small electronic device that is capable of storing and transmitting data wirelessly through radio waves.
Unlike active RFID tags that have an internal power source, passive RFID tags rely on the energy transmitted by an RFID reader to power their operation. When an RFID reader emits a radio frequency signal, the passive RFID tag captures this energy through an antenna and uses it to power the chip inside. This chip then generates a response signal containing its unique information, such as a unique identifier or sensor data, which is sent back to the RFID reader for processing.
Passive RFID tags are typically made up of three main components:
- Chip: The chip, also known as an integrated circuit (IC) or microchip, is responsible for storing and processing the tag’s data. It contains a unique identification number and may have additional memory for storing additional information.
- Antenna: The antenna serves as the communication link between the tag and the RFID reader. It captures the radio frequency energy emitted by the reader and uses it to power the chip and transmit the response signal.
- Substrate: The substrate provides the physical structure and support for the chip and antenna. It is typically made of materials such as plastic or paper, depending on the application and environment in which the tag will be used.
Passive RFID tags come in various shapes, sizes, and form factors to cater to different use cases. They can be as small as a grain of rice or as large as a credit card, depending on the intended application. Some tags are designed to be attached to objects or products, while others can be embedded or integrated into the product itself.
Overall, passive RFID tags are cost-effective, lightweight, and reliable solutions for identification, tracking, and monitoring purposes. They have been widely adopted in industries such as retail, supply chain management, healthcare, and asset tracking, where real-time visibility and efficient data capture are crucial.
Now that we have a solid understanding of what passive RFID tags are and their key components, let’s explore how they actually work in the next section.
How Does a Passive RFID Tag Work?
To understand how a passive RFID tag works, we need to break down the process into three main stages: energizing, modulation, and communication.
1. Energizing: The process begins when an RFID reader emits a radio frequency signal, typically in the range of 860 to 960 MHz. This signal serves to energize the passive RFID tag by providing it with power. The tag’s antenna captures the energy from the radio waves and transfers it to the chip inside the tag.
2. Modulation: Once the passive RFID tag is powered, the chip starts to modulate the energy it receives from the reader’s signal. Modulation involves manipulating the energy to transmit data. The tag’s chip encodes its unique identification number, sensor data, or other stored information into the response signal.
3. Communication: The modulated response signal is then transmitted back to the RFID reader through the tag’s antenna. The reader, which is equipped with its own antenna, captures the response signal and decodes the information encoded by the passive RFID tag. This data can be used for various purposes, such as inventory management, authentication, or tracking.
It’s important to note that the communication between the passive RFID tag and the reader is short-range and relies on proximity. The effectiveness of the communication depends on factors such as the frequency used, the power of the RFID reader, and any physical obstacles or interference in the environment.
Passive RFID tags operate in different frequency bands, including low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF). Each frequency band has its own advantages and limitations. LF tags typically offer a shorter read range and are less susceptible to interference, while UHF tags provide a longer read range and faster data transfer speeds, but can be affected by environmental factors like liquids or metals.
Overall, the working principle of a passive RFID tag revolves around the concept of harnessing energy from an RFID reader’s signal and using that energy to transmit data. This makes passive RFID tags efficient, cost-effective, and reliable solutions for a wide range of applications.
In the next section, we will explore the components that make up a passive RFID tag, shedding light on their functionalities and the role they play in the overall operation of the tag.
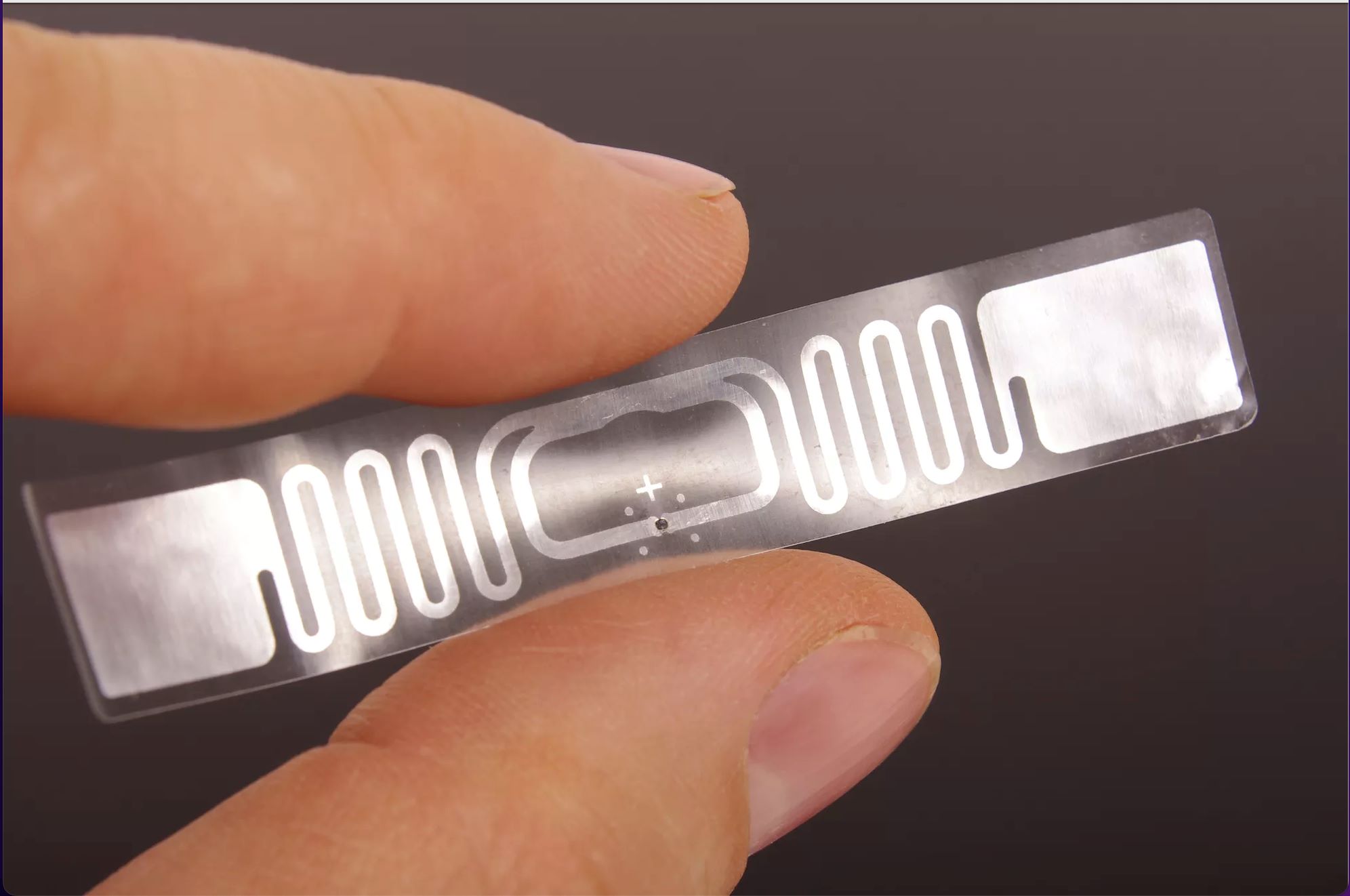
Components of a Passive RFID Tag
A passive RFID tag may appear as a simple device, but it consists of several key components that work together to enable its operation and communication with an RFID reader. Understanding these components is crucial to gain insight into the functionality and capabilities of a passive RFID tag.
1. Chip: The chip, also known as an integrated circuit (IC) or microchip, serves as the brain of the passive RFID tag. It is responsible for storing and processing data. The chip contains a unique identification number, which is commonly referred to as an Electronic Product Code (EPC). Additionally, the chip may have additional memory to store additional information, such as product details or sensor data.
2. Antenna: The antenna acts as the link between the passive RFID tag and the RFID reader. It captures the radio frequency energy emitted by the reader and converts it into electrical power to energize the tag. The antenna also plays a crucial role in transmitting the response signal back to the reader. The design and size of the antenna depend on factors such as the frequency used, read range requirements, and the physical constraints of the application.
3. Substrate: The substrate provides the physical structure and support for the chip and antenna. It is typically made of materials such as plastic or paper, depending on the application and durability requirements. The substrate is responsible for protecting the internal components of the passive RFID tag from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and physical impacts.
4. Enclosure: In some cases, a passive RFID tag may have an enclosure or packaging around its internal components. This enclosure offers additional protection and durability, ensuring the tag’s resilience in challenging environments. Enclosures can vary in form and material, ranging from plastic casings to ruggedized designs for industrial applications.
5. Adhesive or Mounting Mechanism: To attach the passive RFID tag to an object or surface, it may be equipped with an adhesive layer or a mounting mechanism. This allows for easy integration into various products or assets. The adhesive or mounting mechanism should be chosen according to the required durability, ease of attachment, and compatibility with the intended application.
These components work together seamlessly to enable the functionality of a passive RFID tag. The chip stores and processes data, the antenna captures and transmits radio frequency energy, and the substrate and enclosure protect the internal components from environmental factors.
It’s worth noting that the advancement of technology continues to bring innovations to passive RFID tags, leading to the development of more compact, durable, and feature-rich tags. Enhanced features, such as sensors for temperature or humidity monitoring, enable passive RFID tags to provide even more value in a wide range of industries, from supply chain management to healthcare.
In the next section, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of using passive RFID tags, shedding light on why they have gained widespread adoption in various industries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Passive RFID Tags
Passive RFID tags offer numerous advantages that have contributed to their widespread adoption in various industries. However, like any technology, they also have their limitations. In this section, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of using passive RFID tags.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective: Passive RFID tags are relatively inexpensive compared to other tracking and identification technologies. They are cost-effective for large-scale deployments, making them ideal for inventory management and asset tracking applications.
- Longevity: Passive RFID tags have a long lifespan, typically exceeding 10 years. This durability ensures that they can withstand harsh environmental conditions and repeated use.
- No internal power source: One of the notable advantages of passive RFID tags is that they do not require an internal power source. They rely on the energy transmitted by RFID readers, eliminating the need for battery replacements or maintenance.
- Easy integration: Passive RFID tags can easily be integrated into existing systems and processes. They can be attached or embedded onto products, assets, or documents, allowing for seamless tracking and identification without disruption to operations.
- Fast and accurate data capture: Passive RFID technology enables fast and accurate data capture. Multiple tags can be read simultaneously, even in motion, allowing for efficient inventory management and real-time visibility.
- Reduced human error: By automating data capture and eliminating manual processes, passive RFID tags reduce the risk of human error associated with manual data entry or barcode scanning.
Disadvantages:
- Short read range: Compared to active RFID tags, passive RFID tags have a shorter read range. This limitation requires tags to be in close proximity to an RFID reader for effective communication.
- Interference concerns: Passive RFID tags can be affected by interference from surrounding objects, liquids, or metals. This interference can reduce the effectiveness of communication between the tag and the reader.
- Privacy and security: Passive RFID technology raises privacy and security concerns, as the tags can be read without the individual’s knowledge or consent. However, encryption and access control mechanisms can help mitigate these concerns.
- Environmental limitations: The performance of passive RFID tags can be affected by the surrounding environment. Factors such as humidity, temperature, and the presence of liquids or metals can impact the readability and reliability of the tags.
- Initial infrastructure setup: Implementing a passive RFID system may require initial investment in RFID readers, antennas, and software infrastructure. While the cost has significantly decreased over the years, it can still be a barrier for some businesses.
Overall, the advantages of passive RFID tags, such as cost-effectiveness, longevity, and easy integration, make them an attractive choice for various industries. However, it is important to consider the limitations and challenges associated with the technology, such as short read range and privacy concerns, when deciding to implement passive RFID tags.
Next, let’s explore the diverse applications where passive RFID tags have found success.
Applications of Passive RFID Tags
Passive RFID tags have found significant applications across various industries due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of integration. Let’s explore some of the key applications where passive RFID tags have made a significant impact:
- Inventory Management: Passive RFID tags are widely used in inventory management systems to track and manage stock levels. By attaching RFID tags to products or packaging, businesses can easily conduct accurate and efficient inventory audits, reduce stockouts, and streamline supply chain operations.
- Asset Tracking: Organizations across different sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics, utilize passive RFID tags to track and monitor assets such as equipment, tools, and vehicles. This allows them to locate assets quickly, improve asset utilization, and prevent loss or theft.
- Retail: In the retail industry, passive RFID tags play a crucial role in improving inventory accuracy and enhancing the overall shopping experience. Retailers can track item-level information, automate checkout processes, and prevent theft with RFID-enabled systems.
- Access Control: Passive RFID tags are commonly used in access control systems for secure entry and authentication. They enable hands-free access when attached to employee or visitor badges, reducing the need for manual identification and enhancing security measures.
- Document Management: Passive RFID tags help streamline document management processes by enabling efficient tracking and retrieval. They can be embedded in files, folders, or even library books, making it easier to locate and manage important documents.
- Animal Tracking: Passive RFID tags are widely used in agriculture and livestock management for animal identification and tracking. Farmers can easily monitor the health, breeding, and movement of livestock, improving overall farm efficiency and animal welfare.
- Supply Chain Management: Within the supply chain, passive RFID tags enable real-time tracking of shipments, ensuring end-to-end visibility and streamlining logistics operations. This improves inventory accuracy, reduces manual labor, and enhances supply chain efficiency.
- Healthcare: In healthcare settings, passive RFID tags are used for patient identification, medication tracking, and asset management. They enhance patient safety, reduce medication errors, and improve the overall efficiency of healthcare workflows.
These are just a few examples of the many applications where passive RFID tags have proven to be valuable tools. The versatility and adaptability of these tags make them suitable for various industries and use cases, improving efficiency, accuracy, and security.
Next, let’s delve into the challenges and limitations that passive RFID technology faces in certain scenarios.
Challenges and Limitations of Passive RFID Technology
While passive RFID technology offers numerous benefits, it also faces certain challenges and limitations that need to be considered when implementing this technology. Let’s explore some of the key challenges and limitations associated with passive RFID:
- Short Read Range: Passive RFID tags have a limited read range compared to active RFID tags. This means that the tags need to be in close proximity to the RFID reader for successful communication. Factors such as the frequency used and the presence of physical obstacles can further affect the read range.
- Interference and Signal Reflection: RFID signals can be subject to interference from other electronic devices, metals, or liquids in the environment. This can affect the reliability and consistency of communication between the tags and the reader. Signal reflections caused by metal surfaces can also lead to signal distortion and decreased read accuracy.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: Passive RFID tags can be read remotely and without the individual’s knowledge or consent, raising privacy concerns. The transmission of sensitive personal or financial information through RFID tags requires the implementation of encryption and access control mechanisms to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Environmental Limitations: The performance of passive RFID tags can be affected by the surrounding environment. For example, the presence of liquids, metals, or extreme temperatures can impact the readability and reliability of the tags. Specialized tags may be required to overcome these environmental limitations.
- Initial Infrastructure Setup: Implementing a passive RFID system may require an initial investment in RFID readers, antennas, and software infrastructure. While the costs have significantly decreased over the years, the need for infrastructure setup can still be a barrier for some businesses or organizations.
- Data Collision and Read Accuracy: When multiple tags are present within the read range, there is a potential for data collision, where the reader may have difficulty reading and distinguishing individual tags simultaneously. This can result in reduced read accuracy and the need for additional measures to ensure tag identification and data integrity.
Despite these challenges and limitations, passive RFID technology continues to advance and evolve, offering improved performance and addressing some of these concerns. It is essential to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application and mitigate any potential limitations through proper system design and implementation.
Now, let’s wrap up our discussion by summarizing the key points we’ve covered in this article.
Conclusion
Passive RFID tags have revolutionized various industries with their cost-effectiveness, ease of integration, and ability to provide real-time visibility and data capture. Throughout this article, we have explored the definition, functionality, advantages, applications, challenges, and limitations of passive RFID tags.
We started by understanding the basics of passive RFID tags and how they work. We learned that passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source but rely on the energy transmitted by an RFID reader to power their operation. The tags consist of a chip, antenna, and substrate, which work together to enable communication with the reader.
Passive RFID tags offer numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, longevity, and accurate data capture. They find applications in inventory management, asset tracking, retail, access control, and many other industries. However, they also face challenges such as short read range, interference concerns, and privacy considerations.
In conclusion, passive RFID tags have significantly impacted various industries by providing efficient and reliable tracking, identification, and data capture solutions. While they have their limitations, advancements in technology continue to address these challenges and improve the capabilities of passive RFID systems.
It is important for businesses and organizations to carefully consider their specific requirements, environmental factors, and potential limitations when implementing passive RFID technology. By doing so, they can harness the advantages of passive RFID tags and leverage them to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance overall business processes.
As technology continues to evolve, passive RFID tags are expected to play an even greater role in optimizing supply chains, enhancing customer experiences, and contributing to the digital transformation of industries worldwide.

