How To Check RFID Tag Is Working Or Not
Introduction
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has become increasingly popular in various industries for tracking and identifying objects. RFID tags are small electronic devices that use radio waves to transmit data to a reader. These tags are commonly used in applications such as inventory management, access control, and asset tracking. However, it is essential to ensure that RFID tags are functioning correctly to avoid any potential issues or inaccuracies in data collection.
Checking the functionality of RFID tags is crucial because any malfunction or damage can lead to errors in tracking, loss of information, or compromised security. Whether you are using RFID tags for personal or business purposes, understanding how to check if an RFID tag is working is essential to maintain smooth operations.
In this article, we will explore different methods to check the functionality of RFID tags, including visual inspection, using an RFID reader or scanner, and verifying signal strength. We will also discuss common problems that may arise with RFID tags and possible troubleshooting solutions.
By following these guidelines and best practices, you can ensure the proper functioning of RFID tags, improve data accuracy, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Definition of RFID Tag
A Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tag is a small electronic device that contains a microchip and an antenna. It uses radio waves to transmit and receive data wirelessly. The RFID tag is affixed to an object or embedded into a product, allowing for automatic identification and tracking.
The RFID tag consists of two main components: the microchip and the antenna. The microchip contains a unique identifier and can store additional data such as product information or security codes. The antenna is responsible for transmitting and receiving radio waves for communication with RFID readers or scanners.
RFID tags can be classified into two types: passive and active. Passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source and rely on the energy harvested from the RFID reader’s signals to power their operations. They are usually smaller, less expensive, and have a shorter read range. Active RFID tags, on the other hand, have an internal power source, such as a battery, which enables them to actively transmit data over longer distances. Active RFID tags are typically larger, more expensive, and have a longer read range.
RFID technology offers several advantages over traditional barcode systems. Unlike barcodes, which require line-of-sight scanning, RFID tags can be read from a distance and even through non-metallic materials. This enables faster and more efficient inventory management, asset tracking, and supply chain logistics. RFID tags also provide better data accuracy, as they can be read in bulk rather than one at a time like barcodes.
Today, RFID technology is used in various industries, including retail, healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and logistics. It enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Importance of Checking RFID Tag
Checking the functionality of RFID tags is of utmost importance to ensure accurate and reliable data collection and operation. Here are several reasons why it is essential to regularly check RFID tags:
- Data Accuracy: RFID tags are used for tracking and identification purposes. If a tag is not functioning properly, it can lead to inaccurate data collection, which can have significant consequences. For example, in inventory management, an invalid or malfunctioning RFID tag could result in incorrect stock levels, leading to stockouts or overstock situations.
- Operational Efficiency: Functional RFID tags streamline operations by automating processes such as asset tracking, supply chain management, and access control. When RFID tags are not working, these processes may be disrupted, leading to delays, errors, and inefficiencies.
- Security: RFID tags are often used for access control in various environments, such as secure facilities, airports, and hospitals. If an RFID tag is not functioning properly, it can compromise security measures, potentially allowing unauthorized individuals to gain access to restricted areas.
- Cost Savings: Regularly checking RFID tags helps identify any issues early on, allowing for timely repairs or replacements. This proactive approach can prevent costly downtime, minimize disruptions, and save money in the long run.
- Customer Satisfaction: In industries such as retail and e-commerce, RFID tags are utilized to improve inventory accuracy and ensure timely product availability. When RFID tags are functioning correctly, customers can trust that the items they want are in stock, resulting in a positive shopping experience.
By checking the functionality of RFID tags on a regular basis, businesses can avoid potential problems, maintain data accuracy, optimize operations, enhance security, and provide a better overall experience for customers.
Methods to Check RFID Tag
There are various methods available to check the functionality of RFID tags. These methods help ensure that the tags are working correctly and provide accurate data. Here are some common methods to check RFID tags:
- Visual Inspection: The first and simplest method is a visual inspection of the RFID tag. Check for any physical damage, such as cracks, bent antennas, or detached components. Ensure that the tag is firmly attached to the object, especially if it is adhesive-backed. If any visible damage or misplacement is detected, replace or reposition the tag accordingly.
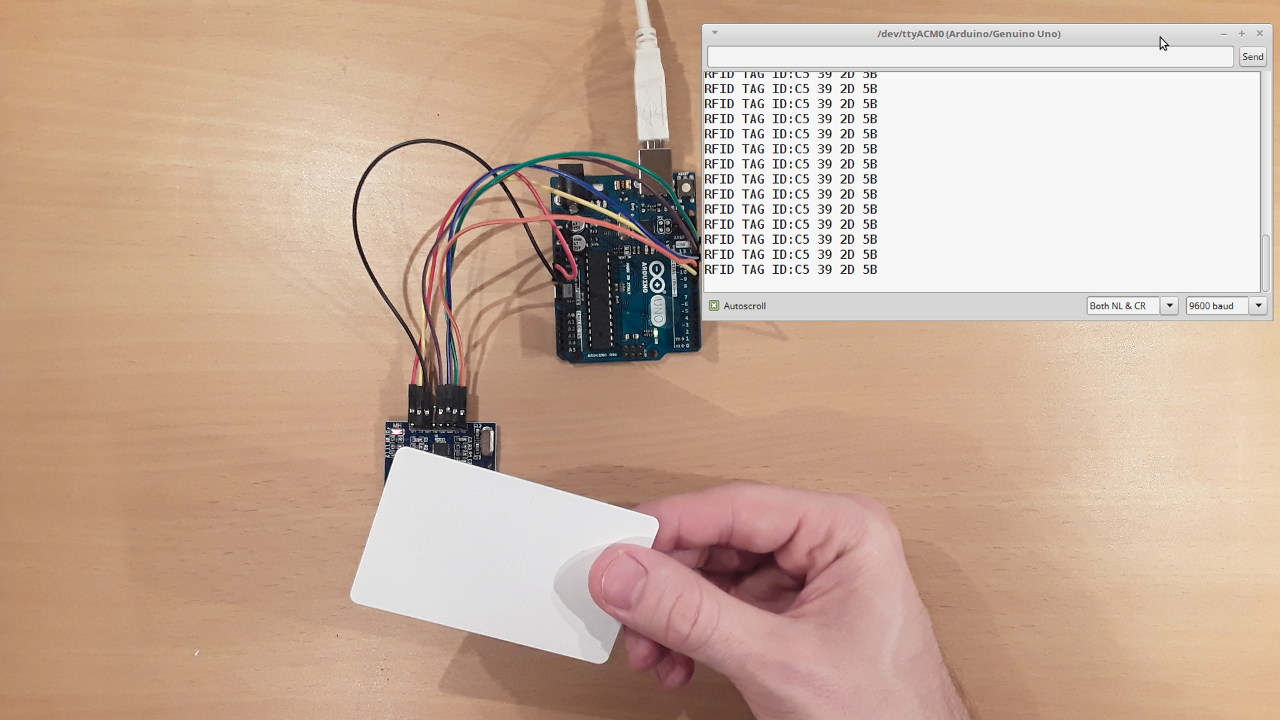
- Checking with RFID Reader: Another method to check RFID tags is to use an RFID reader. Place the tag within the read range of the reader and check if it is detected. The RFID reader will display or transmit the tag’s unique identifier. If the tag is undetectable, it may indicate a problem with the tag, reader, or communication between them.
- Testing with RFID Scanner: RFID scanners are handheld devices used to read and identify RFID tags. By scanning the tag with an RFID scanner, you can verify if it is functioning properly. The scanner will display the tag’s information on its screen or through a connected device. Testing with an RFID scanner allows you to quickly identify any malfunctioning tags.
- Verifying Signal Strength: Signal strength can impact the performance of RFID tags. Use an RFID reader or scanner to check the signal strength of the tag. Move the tag closer to or farther from the reader to observe if the signal strength changes. Low signal strength may indicate tag malfunction, weak antenna, or interference issues that need to be addressed.
These methods can be used individually or in combination, depending on the specific requirements and circumstances. Regularly checking RFID tags using these methods ensures that they are working properly and provides peace of mind in terms of accurate data collection and efficient operations.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is a simple yet essential method to check the functionality of RFID tags. By visually examining the tags, you can identify any physical damage or issues that may affect their performance. Here are some steps to conduct a visual inspection of RFID tags:
- Check for Physical Damage: Inspect the RFID tags for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks, dents, or bent antennas. Damage to the tag can impact its ability to transmit and receive radio waves, resulting in poor performance or complete failure.
- Ensure Firm Attachment: Verify that the RFID tags are securely attached to the objects they are affixed to, especially if they are adhesive-backed. Loose tags may cause inconsistent readings or complete loss of signal. If a tag is loose, reposition or reattach it properly.
- Examine Antenna: Take a closer look at the tag’s antenna. Ensure that it is intact and not damaged. The antenna is a critical component for transmitting and receiving radio waves, and any damage to it can severely affect the tag’s performance.
- Check for Wear and Tear: Over time, RFID tags may experience wear and tear due to environmental factors or regular use. Look for signs of wear, such as fading or peeling. If the tag’s appearance deteriorates, it is recommended to replace it with a new one to maintain optimal performance.
During the visual inspection, make sure to follow any specific guidelines provided by the manufacturer. Some RFID tags may have additional features or indicators that can be examined visually, such as LED lights or tamper-evident features.
By conducting regular visual inspections of RFID tags, you can identify any physical damage or issues early on. Addressing these issues promptly will help ensure that the tags are functioning correctly and prevent potential problems that may arise during tracking, identification, or data collection processes.
Checking with RFID Reader
One effective method to check the functionality of RFID tags is by using an RFID reader. An RFID reader is a device that sends and receives radio frequency signals to communicate with RFID tags. Here is a step-by-step process for checking RFID tags using an RFID reader:
- Power on the RFID Reader: Ensure that the RFID reader is properly powered on and ready for operation. Connect it to a power source or make sure the batteries are fully charged.
- Position the RFID Tag: Place the RFID tag within the read range of the RFID reader. The read range varies depending on the specific reader and tag, so consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for optimal positioning.
- Perform the Reading: Activate the RFID reader to scan for nearby tags. The reader will emit radio frequency signals to communicate with the tags within its range. Once the reader detects a tag, it will display or transmit the tag’s unique identifier or any additional information stored on the tag.
- Check for Successful Reading: Confirm that the RFID reader successfully reads the RFID tag’s information. If the reader successfully reads the tag’s data, it indicates that the tag is functioning properly. However, if the tag is not detected or the data cannot be read, it may suggest a problem with the tag, reader, or the communication between them.
- Repeat for Multiple Tags: If you are checking multiple RFID tags, repeat the process for each tag individually. This will help identify any tags that are not properly detected or are malfunctioning.
It is important to note that different RFID readers and tags may have varying compatibilities and specifications. Ensure that the RFID reader you are using is compatible with the specific tag technology being used.
By utilizing an RFID reader to check RFID tags, you can quickly and accurately determine if the tags are working as intended. This method allows for efficient identification and troubleshooting of any malfunctioning or undetected tags, improving overall operational efficiency and data accuracy.
Testing with RFID Scanner
Another effective method to check the functionality of RFID tags is by using an RFID scanner. An RFID scanner is a handheld device that can read and identify RFID tags. It offers a portable and convenient way to test the performance of RFID tags. Here is a step-by-step process for testing RFID tags using an RFID scanner:
- Power on the RFID Scanner: Ensure that the RFID scanner is powered on and ready for operation. Charge the batteries or connect it to a power source to ensure sufficient power.
- Position the RFID Tag: Hold the RFID scanner in close proximity to the RFID tag being tested. The scanner should be within the read range specified by the manufacturer of the scanner and tag.
- Scan the RFID Tag: Activate the scanning function on the RFID scanner. Place the scanner’s antenna near or directly on the RFID tag to initiate the scanning process. The scanner will emit radio frequency signals to communicate with the tag and retrieve its unique identifier or any additional information stored on the tag.
- Check the Scanned Information: Verify that the RFID scanner successfully reads the information from the RFID tag. Look for the tag’s unique identifier or any other relevant data displayed on the scanner’s screen or transmitted to an external device. If the scanned information is displayed correctly, it indicates that the RFID tag is functioning properly. However, if no information is detected or the data appears incorrect, it may suggest an issue with the tag’s functionality.
- Repeat for Multiple Tags: If you are testing multiple RFID tags, repeat the scanning process for each tag one by one. This allows you to identify any tags that are not being properly scanned or are malfunctioning.
Using an RFID scanner provides a portable and efficient way to test the functionality of RFID tags. It allows you to quickly determine if the tags are working correctly and retrieve the necessary information. This method is especially useful when dealing with a large number of tags or when conducting on-the-go testing in various locations.
Remember to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations when using specific RFID scanner models to ensure accurate testing and reliable results.
Verifying Signal Strength
Verifying the signal strength of RFID tags is an important method to check their functionality. The signal strength can indicate the quality of the communication between the RFID reader and the tag. Here’s a step-by-step process for verifying the signal strength of RFID tags:
- Position the RFID Tag: Place the RFID tag within the read range of the RFID reader, ensuring that it’s in an optimal position for communication. The read range can vary depending on the specific reader and tag, so refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended distance.
- Observe the Signal Strength: Use the RFID reader’s signal strength indicator or software to monitor the signal strength of the tag. The indicator may display a signal bar, numeric value, or provide visual cues such as color-coding.
- Move the Tag Closer or Farther: Gradually move the RFID tag closer to or farther away from the RFID reader while observing the changes in signal strength. Note any significant fluctuations or drops in signal strength as you adjust the distance.
- Assess the Signal Strength: Evaluate the signal strength readings obtained during the movement of the RFID tag. Ideally, a strong signal strength indicates proper functionality, while weak signals may suggest issues such as tag malfunction, poor antenna quality, or interference in the environment.
- Record and Compare the Results: Keep a record of the signal strength readings for each RFID tag. Compare the readings to establish a baseline and identify any tags with consistently weak signals or significant variations in signal strength.
Verifying the signal strength of RFID tags helps in identifying potential problems and optimizing their performance. If you encounter weak signal strength, you may need to address issues such as tag replacement, adjusting the reader’s position, using repeaters or amplifiers, or resolving environmental interference.
It’s important to note that different RFID readers and tags may have varying sensitivities and signal strength indicators. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to interpret the signal strength readings accurately.
By actively verifying and monitoring the signal strength of RFID tags, you can ensure robust and reliable communication between the tags and the readers, leading to accurate data collection and improved operational efficiency.
Troubleshooting RFID Tag Issues
Despite their reliability, RFID tags may encounter issues that affect their functionality. Troubleshooting RFID tag issues is crucial to identify and resolve any problems that may arise. Here are some common troubleshooting steps to address RFID tag issues:
- Ensure Proper Placement: Verify that the RFID tag is correctly positioned according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Incorrect placement can lead to weak signal strength or improper detection. Reposition the tag if necessary and test for improved performance.
- Check for Interference: Environmental factors, such as metallic objects, electromagnetic interference, or nearby electronic devices, can disrupt RFID communication. Remove any potential sources of interference and test the tag’s functionality in a clear environment.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: If the RFID tags are wired or connected to external devices, check for loose or damaged connections. Ensure that all wiring is intact and properly connected, as faulty connections can hinder proper tag functionality.
- Replace Dead or Weak Batteries: If you are using active RFID tags with internal batteries, check the battery levels or replace them if they are dead or weak. Low battery power can cause communication issues and affect the performance of active tags.
- Upgrade Firmware or Software: In some cases, RFID tags may require firmware updates or software patches to address bugs or improve functionality. Consult the tag manufacturer’s documentation for any available updates and follow the provided instructions to ensure optimal performance.
- Test with Different Readers or Scanners: If you suspect a problem with the RFID reader or scanner, try testing the tag with a different reader or scanner. This helps isolate the issue and determine whether it lies with the tag or the reader/scanner.
If the troubleshooting steps above do not resolve the RFID tag issue, consider contacting the tag manufacturer’s technical support for assistance. They can provide further guidance and troubleshooting specific to their product.
Regular maintenance and monitoring of RFID tags can help prevent issues from arising. Additionally, it is important to keep a record of any troubleshooting steps taken, as well as the outcomes, to aid in future problem-solving efforts.
By following these troubleshooting steps and promptly addressing any issues that arise, you can ensure smooth and reliable operation of RFID tags, minimizing disruptions and maintaining accurate data collection.
Common Problems and Solutions
While RFID technology is generally reliable, there are some common problems that can occur with RFID tags. Understanding these problems and their solutions can help troubleshoot and resolve any issues that may arise. Here are some of the most common problems associated with RFID tags:
- Tag Not Detected: One common issue is when an RFID tag is not detected by the reader or scanner. This could be due to a weak signal, misalignment, or interference. To resolve this, ensure proper tag placement, adjust the reader position, and eliminate any sources of interference.
- Interference: Interference from other electronic devices, metal objects, or environmental factors can disrupt RFID communication. To overcome this issue, remove or relocate potential sources of interference, or consider using shielding to protect the tags from external interference.
- Read Range Issues: A limited read range can impact the effectiveness of RFID tags. This can happen due to weak signal strength, low battery power in active tags, or obstacles obstructing the signal. To address this problem, optimize the tag-reader distance, ensure adequate power for active tags, and remove any interfering objects.
- Data Integrity: Inaccurate or corrupted data can occur when RFID tags experience interference or error during data transmission. Implementing error-checking mechanisms, using redundancy in data storage, or adopting encryption measures can help ensure data integrity and minimize errors.
- Tag Collision: Tag collision happens when multiple tags respond simultaneously, causing interference and unreadable data. Anti-collision protocols, such as the Electronic Product Code (EPC) Gen2, are designed to mitigate this issue by allowing simultaneous reading of multiple tags through backscatter modulation techniques.
- Environmental Factors: Extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or physical stress can impact the performance and durability of RFID tags. Selecting tags suitable for the intended environment and ensuring their compatibility with the conditions they will be exposed to can prevent problems related to environmental factors.
To address these common problems, it is crucial to follow best practices, implement proper tag placement, use appropriate tag-reader configuration, conduct regular maintenance, and ensure compatibility between the tags and the environment they will be deployed in.
If persistent problems occur or if you are experiencing difficulties diagnosing and resolving issues, consider consulting with RFID experts or contacting the tag manufacturer’s technical support for further assistance.
By being aware of these common problems and their solutions, you can effectively mitigate issues and ensure the smooth functioning of RFID tags, improving operational efficiency and data accuracy.
Conclusion
Successfully checking the functionality of RFID tags is crucial for businesses and organizations to ensure accurate data collection, efficient operations, and enhanced security. By employing various methods such as visual inspection, using RFID readers or scanners, verifying signal strength, and troubleshooting common issues, you can maintain the optimal performance of RFID tags.
Visual inspection allows for the identification of any physical damage or misplacement of RFID tags. Checking with RFID readers and scanners enables the detection of tags and the retrieval of their unique identifiers or additional information. Verifying signal strength allows for understanding the quality of communication between RFID tags and readers, while troubleshooting provides solutions to common issues that may arise.
Regularly checking RFID tags and addressing any issues promptly ensures data accuracy, operational efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. It also helps prevent potential disruptions and security breaches. By following best practices and staying informed about the specific requirements of RFID tag technology, you can maximize the benefits derived from their usage.
Remember to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and seek technical support when necessary to ensure proper functionality and performance. With proper maintenance, monitoring, and troubleshooting, RFID tags will continue to provide seamless tracking, identification, and data collection capabilities across a wide range of industries.

