How Long Is The Texas-Mexico Border?
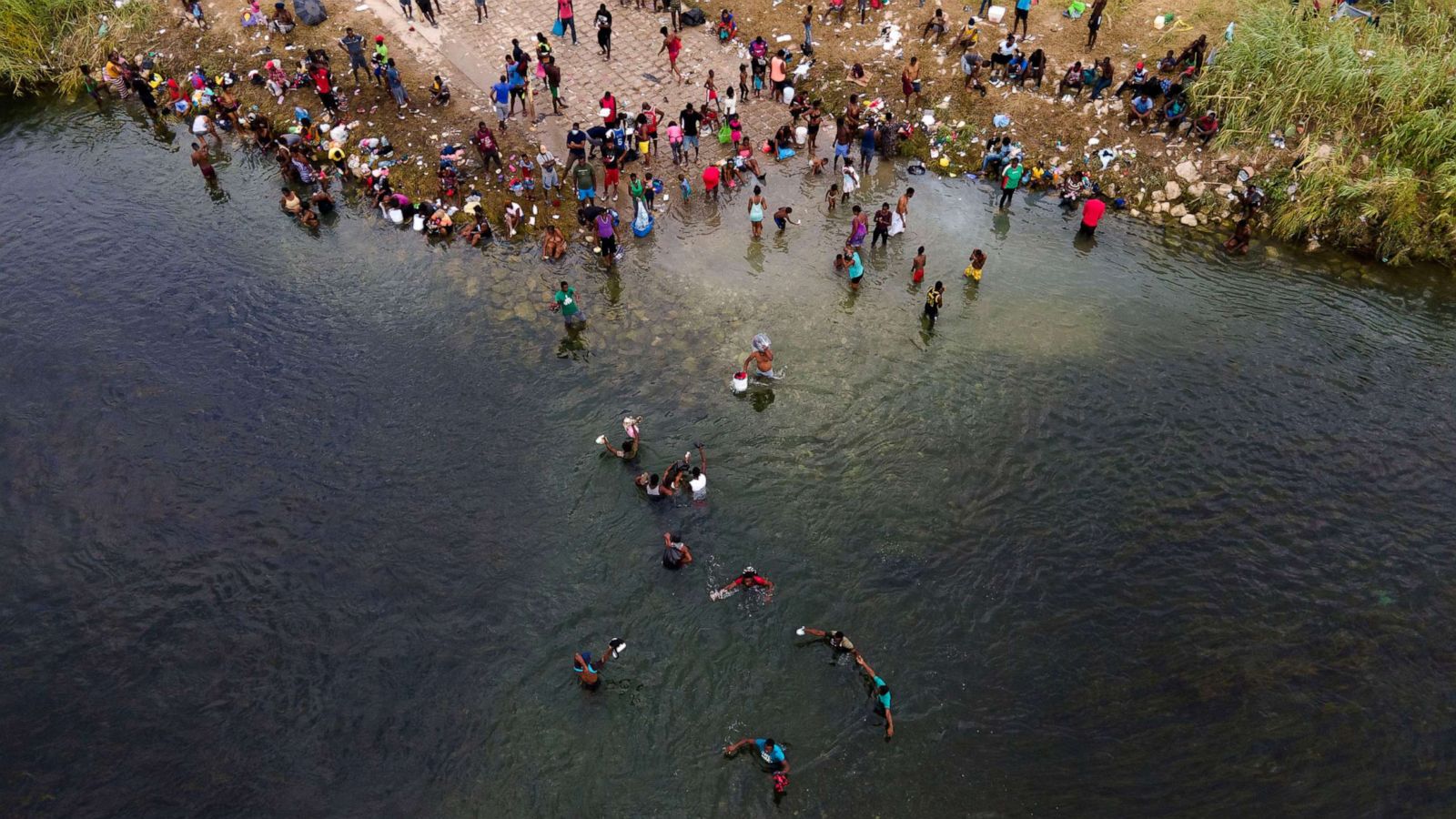
Introduction
Welcome to the Lone Star State, where everything is bigger, including its borders. Texas, the second-largest state in the United States, shares a lengthy border with Mexico. The Texas-Mexico border is not only significant in terms of its physical length, but it also holds historical, cultural, and economic importance.
Stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to the southwestern corner of Texas, the border is a convergence of two distinct cultures, blending the Texan charm with the vibrant Mexican heritage. The border region is an embodiment of diversity, encompassing bustling cities, rural landscapes, and picturesque landscapes.
Over the years, the Texas-Mexico border has witnessed the ebb and flow of people, goods, ideas, and challenges. From the establishment of Spanish missions and settlements in the 18th century to the modern-day immigration complexities, the border has played a significant role in shaping the history and identity of both Texas and Mexico.
With its robust economy and strategic geographic location, Texas has become a gateway for trade and commerce between the United States and Mexico. The border region serves as a crucial link in the supply chains of various industries, from agriculture to manufacturing. The flow of goods and services across the border boosts the economies of both Texas and Mexico, fostering growth and employment opportunities.
However, the Texas-Mexico border is not without its challenges. It has been a focal point in discussions surrounding border security and immigration policies. Efforts to ensure the safety and integrity of the border have led to increased surveillance, border patrol presence, and the construction of physical barriers.
Furthermore, the border region is home to a unique ecosystem, rich in biodiversity and natural resources. Environmental concerns, such as water usage, pollution, and the impact of border infrastructure, are crucial factors to consider in the development and maintenance of the region.
Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of the Texas-Mexico border. From its historical significance to its economic impact, cultural relevance, and the ongoing challenges it faces, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable border region.
Historical Background
The history of the Texas-Mexico border can be traced back to the early Spanish exploration and colonization of the region. In the 16th century, Spanish conquistadors, led by the likes of Cabeza de Vaca and Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, embarked on expeditions to claim new territories in North America. They ventured into what is now Texas, establishing the first European presence in the area.
The 18th century saw the establishment of Spanish missions and settlements along the border. These missions aimed to convert the indigenous population to Christianity while also serving as a line of defense against French incursions from the east. Presidios, or military forts, were also built to protect the region from indigenous tribes and other potential invaders.
During the Mexican War of Independence in the early 19th century, Mexico gained its independence from Spain. The newly formed Mexican government inherited the territory of Texas, which included the land that would later become the Texas-Mexico border.
In the Texas Revolution of 1835-1836, Texan settlers fought against Mexican rule and declared their independence. This led to the establishment of the Republic of Texas, separate from Mexico. However, tensions between Texas and Mexico persisted, leading to the Mexican-American War in 1846.
The outcome of the Mexican-American War solidified the borders between the two nations. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed in 1848, established the Rio Grande River as the official border between Texas and Mexico. This international boundary remains unchanged to this day.
Throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the border region experienced significant changes, as Texas became part of the United States and Mexico underwent its own political and social transformations. Civil wars, revolutions, and economic upheavals influenced the dynamics of the border region, shaping its diverse cultural landscape.
In recent decades, the Texas-Mexico border has become a focal point in discussions surrounding immigration and security. The increase in cross-border trade and the movement of people has led to evolving policies and debates about border control and the challenges associated with illegal immigration and drug smuggling.
Understanding the historical background of the Texas-Mexico border is crucial to comprehending the complexities and significance of this region. It provides a context for the cultural blending, economic ties, and ongoing border challenges that shape the present-day reality along this lengthy international boundary.
Physical Length of Texas-Mexico Border
The Texas-Mexico border is one of the longest international borders in the world, stretching approximately 1,254 miles (2,018 kilometers) from the Gulf of Mexico to the Four Corners region. The border follows the course of the Rio Grande River, marking the division between Texas and Mexico.
The Rio Grande, known as the Rio Bravo in Mexico, serves as a natural boundary for much of its length. The river cuts through canyons, meanders across plains, and winds its way through deserts, offering a stunning backdrop as it defines the boundary between the two nations.
However, due to the dynamic nature of rivers and the shifting of their banks over time, the precise border line is subject to change. This has led to occasional disputes and negotiations between the United States and Mexico regarding the exact position of the border.
Along the Texas-Mexico border, there are several ports of entry that serve as official crossings for people and goods. These ports facilitate trade, tourism, and the movement of individuals between the two countries. They are essential hubs for economic and cultural exchange, connecting communities on both sides of the border.
The border region is characterized by a diverse topography, ranging from coastal marshes and plains to rugged mountains and desert landscapes. This variation in terrain adds to the complexity and richness of the Texas-Mexico border. It presents unique opportunities for outdoor recreation, such as birdwatching, hiking, and exploring historical sites.
The physical length of the Texas-Mexico border not only defines the boundaries of these two nations, but it also acts as a bridge between two distinct cultures. The border region serves as a meeting point for Texan and Mexican traditions, customs, and languages. It is a place where diversity thrives, offering a unique blend of cultural experiences.
Understanding and appreciating the physical length of the Texas-Mexico border is essential in comprehending the scale and significance of this region. It represents more than just a line on a map – it is the foundation for a vibrant and dynamic cross-border relationship that continues to evolve.
Border Security and Challenges
The Texas-Mexico border has long been a topic of discussion when it comes to border security and immigration policies. With its vast length and diverse terrain, ensuring the safety and integrity of the border is a complex task. Several challenges and issues present themselves in managing and securing this extensive frontier.
One of the main challenges along the Texas-Mexico border is illegal immigration. As a border state, Texas experiences a significant influx of undocumented immigrants attempting to cross into the United States. The push and pull factors driving migration differ from person to person, but issues such as economic opportunities, political unrest, and family reunification often play a role.
To address these challenges, the United States has implemented various measures to secure the border. This includes increasing the number of Border Patrol agents, using surveillance technology, and constructing physical barriers such as fences and walls in certain areas. The goal is to deter unauthorized entry and prevent criminal activities such as drug trafficking and human smuggling.
However, border security efforts have sparked debates and controversies. Critics argue that some measures, particularly the construction of physical barriers, can harm the environment, disrupt wildlife migration patterns, and hinder cross-border cooperation and collaboration. Balancing security concerns with environmental conservation and community relations remains a complex task.
Furthermore, the Texas-Mexico border is prone to violence and criminal activities related to drug cartels and organized crime. The smuggling of drugs, weapons, and contraband poses a significant challenge to law enforcement agencies on both sides of the border. Cooperation and coordination between U.S. and Mexican authorities are crucial in addressing these transnational criminal activities.
Another challenge is the humanitarian aspect of border security. The border region often becomes a focal point for sheltering and processing individuals seeking asylum or refugee status. Providing adequate care and support to these vulnerable populations is a complex task that requires collaboration between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and international partners.
It is important to approach border security and immigration challenges with humanity and a holistic understanding of the complex factors driving migration. Solutions should consider the economic, social, and political realities on both sides of the border, while also prioritizing the safety and well-being of all individuals involved.
As the border security landscape continues to evolve, ongoing discussions and policies will shape the future of the Texas-Mexico border. The challenge lies in finding a balance between security measures, economic cooperation, and the preservation of cultural and environmental integrity along this diverse and dynamic boundary.
Economic Impact
The Texas-Mexico border is not only a geographical divide but also a hub of economic activity and cross-border trade. The proximity to Mexico, one of the United States’ largest trading partners, creates a dynamic and interconnected economic relationship with significant impact on both sides of the border.
Trade between Texas and Mexico is a vital component of the state’s economy. The border region serves as a gateway for various industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, energy, and tourism. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Texas-Mexico trade accounted for over $200 billion in goods in 2020, making it a crucial economic driver for both entities.
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which has been superseded by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), has further facilitated the flow of goods and services across the border. This agreement has helped to eliminate trade barriers and promote economic integration between the two nations.
In Texas, industries such as automotive manufacturing, electronics, energy, and agriculture heavily rely on trade with Mexico. Many companies have established supply chains that span both sides of the border, taking advantage of the cost efficiencies and specialized skills available in the region.
As goods flow across the border, they generate employment opportunities and contribute to local economies on both sides. The presence of manufacturing plants, maquiladoras, in the border region is a significant employer, providing jobs for many residents in both Texas and Mexico.
The Texas-Mexico border also fosters a vibrant tourism industry. Visitors are drawn to the unique cultural experiences and natural beauty found in both Texas and Mexico. Tourists enjoy exploring historical sites, enjoying diverse cuisine, and experiencing world-class beaches on the Gulf Coast.
Additionally, the border region benefits from cross-border shoppers who take advantage of lower prices and a wider variety of products. Shopping destinations and outlets in border towns attract visitors from both the United States and Mexico, boosting local economies and supporting small businesses.
It’s important to note that the economic impact of the Texas-Mexico border extends beyond trade and tourism. The presence of a diverse population and cultural exchange enriches the region economically. From local restaurants and festivals to language schools and arts and crafts, the fusion of Texan and Mexican cultures creates unique business opportunities and contributes to the overall vibrancy of the border region.
The economic interdependence between Texas and Mexico highlights the significance of the Texas-Mexico border in fostering trade, job creation, and economic development. As policies and agreements continue to shape the cross-border relationship, maintaining a balance between economic integration and protecting the interests of both nations will be crucial.
Environmental Concerns
The Texas-Mexico border is not just a political and economic divide but also an ecologically rich and diverse region. It is home to a unique ecosystem that supports a wide range of flora and fauna. However, the border’s environmental integrity faces several challenges that require careful attention and management.
One of the primary environmental concerns along the Texas-Mexico border is water management. The Rio Grande River, which serves as the border between the two countries, is a vital water source for both Texas and Mexico. Ensuring a fair and sustainable distribution of water resources is essential to support agriculture, maintain ecosystems, and meet the water needs of border communities.
The construction of physical barriers along the border can also have significant environmental implications. These barriers have the potential to disrupt natural habitats, alter wildlife migration patterns, and impede the flow of water. Environmental organizations and conservationists advocate for considering alternative solutions that minimize the impact on wildlife and ecosystems.
The border region is home to various unique and sensitive habitats, including wetlands, coastal areas, deserts, and mountain ranges. Protecting these habitats and the biodiversity they support is crucial. Efforts to conserve and restore these ecosystems are ongoing, with organizations working to preserve endangered species, restore natural waterways, and combat invasive species.
Climate change is another pressing environmental concern for the Texas-Mexico border. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events pose challenges to the region’s ecosystems and communities. Adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change require collaborative efforts and sustainable practices that consider the unique vulnerabilities of the border region.
The development and growth of border communities can also have environmental implications. Urbanization and infrastructure projects can lead to habitat loss, increased pollution, and strains on natural resources. Adopting sustainable practices and using innovative approaches in urban planning can help mitigate these environmental impacts.
Efforts to address environmental concerns on the Texas-Mexico border involve collaboration between federal, state, and local authorities, as well as NGOs and community groups. International cooperation is also crucial, as environmental issues do not abide by national boundaries.
Recognizing the environmental challenges and finding a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability is essential for the long-term well-being of the Texas-Mexico border region. By implementing conservation measures, promoting sustainable development, and incorporating science-based approaches, the border region can maintain its ecological richness while continuing to support the communities that call it home.
Cultural Significance
The Texas-Mexico border is a vibrant confluence of cultures, representing a blending of Texan and Mexican traditions, customs, and languages. The cultural significance of this region is evident in its art, music, cuisine, and festivals, reflecting the rich heritage of both Texas and Mexico.
The borderlands have a long history of cultural exchange and mutual influence. From the Spanish colonization of the region to the establishment of missions and settlements, the Texan and Mexican cultures intertwined, shaping the unique identity of the border region. The influence of Mexican culture can be seen in Tex-Mex cuisine, the prevalence of Spanish language, and the colorful celebrations of Mexican festivals such as Cinco de Mayo and Día de los Muertos.
Traditions and customs are passed down through generations, creating a cultural tapestry that embraces diverse communities and celebrates their shared heritage. The Texas-Mexico border is a melting pot of peoples and traditions, where Texan, Mexican, Hispanic, and Indigenous cultures blend together to create a vibrant and distinctive cultural mosaic.
Music is an essential aspect of the border region’s cultural significance. From traditional Mexican folk songs to the sounds of Texan country and Tejano music, the music scene along the border mirrors the diverse cultural roots of the area. Influential musicians such as Selena Quintanilla, Doug Sahm, and Flaco Jiménez have emerged from this region, leaving a lasting impact on both Texan and Mexican music.
Artistic expression is another manifestation of the cultural significance of the borderlands. Artists draw inspiration from the region’s landscapes, history, and cultural diversity. Public art installations, murals, and galleries showcase the creativity and talent of local artists, contributing to the vibrancy of the border cities.
Cuisine is a key element of cultural identity in the Texas-Mexico border region. Tex-Mex cuisine, which combines elements of Mexican and Texan culinary traditions, has gained international recognition. From mouth-watering tacos and enchiladas to sizzling fajitas and flavorful chili, the region’s cuisine reflects the fusion of flavors and culinary practices.
Moreover, the Texas-Mexico border is home to several annual festivals and cultural events that celebrate the region’s rich heritage. Festivals such as the Charro Days Fiesta in Brownsville, Dia de los Muertos celebrations in various communities, and the Border Folk Festival in El Paso showcase the cultural diversity and serve as opportunities for people to come together and share their traditions.
The cultural significance of the Texas-Mexico border extends beyond its geographical boundaries. Its impact is felt not just in the border cities, but also in other parts of Texas and Mexico. The border has inspired literary works, influenced fashion trends, and fostered cross-cultural collaborations in various artistic fields.
Embracing and celebrating the cultural significance of the Texas-Mexico border helps to promote understanding, appreciation, and unity among diverse communities. It is a reminder that despite our differences, we share a common bond and history that shapes our collective identity in this vibrant and dynamic region.
Conclusion
The Texas-Mexico border is a fascinating and dynamic region that encompasses more than just a physical divide between two nations. It represents a convergence of cultures, a hub of economic activity, a focal point for environmental concerns, and a source of inspiration for art and music.
Throughout history, the Texas-Mexico border has played a pivotal role in shaping the identity, history, and development of both Texas and Mexico. It has witnessed the ebb and flow of people, goods, and ideas, leaving a lasting impact on the region and its communities.
The length and physical features of the Texas-Mexico border contribute to its strategic importance for trade and commerce. The cross-border flow of goods and services boosts economies, creates employment opportunities, and fosters cultural exchange.
However, the border also faces challenges, especially regarding border security, immigration policies, and environmental conservation. Finding a balance between security measures, humanitarian concerns, and environmental considerations remains an ongoing task.
The cultural significance of the Texas-Mexico border is evident in its art, music, cuisine, and festivals. It serves as a meeting ground for Texan and Mexican traditions, celebrating the diversity and rich heritage of the border communities.
In conclusion, the Texas-Mexico border is much more than a political divide. It represents a tapestry of cultures, a reminder of shared history, and a nexus of economic and environmental interdependence. By understanding and appreciating its complexities, we can better embrace the unique character and contributions of this remarkable border region.

